


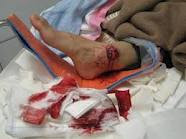
Fracture facts
Introduction to fracture
What causes a fracture?
What are common types of fractures?
Stress fracture
Compression fracture
Rib fracture
Skull fracture
Fracture in children
How is a fracture diagnosed?
What is the treatment for a fracture?
Patient Discussions: Fracture - Causes
Patient Discussions: Fracture - Describe Your Experience
Find a local Doctor in your town
Fracture
Common Types and Locations of Fractures
There are a variety of types and locations that bone fractures that can occur. Common types and locations of fractures include:
greenstick fracture,
spiral fracture,
comminuted fracture,
transverse fracture,
compound fracture,
vertebral compression fracture,
stress fracture,
compression fracture,
rib fracture, and
skull fracture.
Fracture facts
Bone fracture, broken bone, bone crack all mean he same thing. The bone has been damaged such that. None of these terms indicate the severity of the bone damage.
Bones are the body's storage place for calcium. Under hormone control, calcium content of bone is constantly increasing or decreasing.
Bones break when they cannot withstand a force or trauma applied to them. Sometimes the bones are so weak that force may be just gravity, like compression fractures of the back in the elderly.
Fracture descriptions help explain how the breakage appears. For examples, whether or not the fragments are aligned (displaced fracture) and whether or not there is skin overlying the injury is damaged (compound fracture).
Fractures may be complicated by damage to nearby blood vessels, nerves and muscles and joints.
Children's fractures may be more difficult to diagnose because their bones lack enough calcium to be seen on X-ray and because growth plates in the bones may disguise or hide the fracture.
Diagnosis of a fracture includes a history and physical examination. X-rays are often taken. Occasionally, CT or MRI is used to find an occult or hidden fracture or provide more information regarding the damage to the bone and adjacent tissues.
Fractures of the skull, spine and ribs have their own unique diagnosis and treatment issues.
Introduction to fracture
Bones form the skeleton of the body and allow the body to be supported against gravity and to move and function in the world. Bones also protect some body parts, and bone marrow is the production center for blood products.
Bone is not a stagnant organ. It is the body's reservoir of calcium and is always undergoing change under the influence of hormones. Parathyroid hormone increases blood calcium levels by leeching calcium from bone, while calcitonin has the opposite effect, allowing bone to accept calcium from the blood.
What causes a fracture?
When outside forces are applied to bone it has the potential to fail. Fractures occur when bone cannot withstand those outside forces. Fracture, break, or crack all mean the same thing. One term is not better or worse than another. The integrity of the bone has been damaged and the bone structure fails and a fracture occurs.
Broken bones hurt for a variety of reasons including:
The nerve endings that surround bones contain pain fiber. These fibers may become irritated when the bone is broken or bruised.
Broken bones bleed, and the blood and associated swelling (edema) causes pain.
Muscles that surround the injured area may go into spasm when they try to hold the broken bone fragments in place, and these spasms may cause further pain.
Often a fracture is easy to detect because there is obvious deformity. However, at times it is not easily diagnosed. It is important for the physician to take a history of the injury to decide what potential problems might exist. Moreover, fractures don't always occur in isolation, and there may be associated injuries that need to be addressed.
Fractures can occur because of direct blows, twisting injuries, or falls. The type of forces or trauma applied to the bone may determine what type of injury that occurs. Some fractures occur without any obvious trauma due to osteoporosis, the loss of calcium in bone (for example a compression fracture of the vertebrae of the back).
Descriptions of fractures can be confusing. They are based on:
Where in the bone the break has occurred
How the bone fragments are aligned
Whether any complications exist
Whether the skin is intact
The first step in describing a fracture is to decide if it is open or closed. If the skin over the break is disrupted, then an open fracture exists. The skin can be cut, torn, or abraded (scraped), but if the skin's integrity is damaged, the potential for an infection to get into the bone exists. Since the fracture site in the bone communicates with the outside world, these injuries often need to be cleaned out aggressively and many times require anesthesia in the operating room to do the job effectively. Compound fracture was the previous term used to describe an open fracture.
Next, there needs to be a description of the fracture line. Does the fracture line go across the bone (transverse), at an angle (oblique) or does it spiral? Is the fracture in two pieces or is it comminuted, in multiple pieces?
A greenstick fracture describes the situation when the bone partially breaks. This often occurs in infants and children where the bone hasn't completely calcified and has the potential to bend instead of breaking completely through. It is similar to trying to break off a young branch or shoot from a tree (a green stick). Other fracture terms include torus or buckle fracture, again when only part of a bone breaks, but this may occur in adults as well.
Finally, the fracture's alignment is described as to whether the fracture fragments are displaced or in their normal anatomic position. If the bones fragments aren't in the right place, they need to be reduced or placed back into their normal alignment.
In the U.S., more than 2,000 people are with bone cancer every year. There are many types of bone cancer. The most common forms of bone cancer are osteosarcoma, Ewing's sarcoma, chondrosarcoma, malignant fibrous histiocytoma, fibrosarcoma, and chordoma. Pain is the most common symptom. Treatment usually involves surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
Foot Pain
Foot pain may be caused by injuries (sprains, strains, bruises, and fractures), diseases (diabetes, Hansen disease, and gout), viruses, fungi, and bacteria (plantar warts and athlete's foot), or even ingrown toenails. Pain and tenderness may be accompanied by joint looseness, swelling, weakness, discoloration, and loss of function. Minor foot pain can usually be treated with rest, ice, compression, and elevation and OTC medications such as acetaminophen and ibuprofen. Severe pain should be treated by a medical professional.
Pulmonary Embolism (Blood Clot in the Lung)
A pulmonary embolism occurs when a piece of a blood clot from deep vein thrombosis (DVT) breaks off and travels to an artery in the lung where it blocks the artery and damages the lung. The most common symptoms of a pulmonary embolism are shortness of breath, chest pain, and a rapid heart rate.
Elbow Pain
Elbow pain is most often the result of tendinitis, which can affect the inner or outer elbow. Treatment includes ice, rest, and medication for inflammation. Inflammation, redness, warmth, swelling, tenderness, and decreased range of motion are other symptoms associated with elbow pain. Treatment for elbow pain depends upon the nature of the patient's underlying disease or condition.
Ankle Pain and Tendinitis
Ankle pain is commonly due to a sprain or tendinitis. The severity of ankle sprains ranges from mild (which can resolve within 24 hours) to severe (which can require surgical repair). Tendinitis of the ankle can be caused by trauma or inflammation.
Torn Meniscus
A torn meniscus (knee cartilage) may be caused by suddenly stopping, sharply twisting, or deep squatting or kneeling when lifting heavy weight. Symptoms of a meniscal tear include pain with running or walking long distances, popping when climbing stairs, a giving way sensation, locking, or swelling. Treatment depends upon the severity, location, and underlying disease of the knee joint.
oreSacroiliac Joint Dysfunction (SI Joint Pain)
Sacroiliac joint (SI) dysfunction is a general term to reflect pain in the SI joints. Causes of SI joint pain include osteoarthritis, abnormal walking pattern, and disorders that can cause SI joint inflammation including gout, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and ankylosing spondylitis. Treatment includes oral medications, cortisone injections, and surgery.
Anorexia
Anorexia is an eating disorder characterized by markedly reduced appetite or total aversion to food. Anorexia is a serious psychological disorder and is a condition that goes well beyond out-of-control dieting. With anorexia, the drive to become thinner is actually secondary to concerns about control and/or fears relating to one's body. There are psychological and behavioral symptoms as well as physical symptoms of anorexia including: depression, social withdrawal, fatigue, food obsession, heart and gastrointestinal complications, kidney function, flaky skin, brittle nails, and tooth loss (this list is not exhaustive).
Hematoma
A hematoma is a collection of blood that is outside a blood vessel. There are different areas where hematomas occur including the inside the skull, scalp, ear, septum, bones, finger and toenails, and intra-abdominal. Treatment for hematomas depend on the type and location of the hematoma.
Chest Pain
Chest pain is a common complaint by a patient in the ER. Causes of chest pain include broken or bruised ribs, pleurisy, pneumothorax, shingles, pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, angina, heart attack, costochondritis, pericarditis, aorta or aortic dissection, and reflux esophagitis. Diagnosis and treatment of chest pain depends upon the cause and clinical presentation of the patient's chest pain.
Multiple Myeloma
Multiple myeloma is a form of cancer that develops in plasma cells, the white blood cells that make antibodies. Symptoms include bone pain, weakness, extreme thirst, nausea, frequent urination, and broken bones. Treatment of multiple myeloma depends upon the staging and symptoms of the disease.
Internal Bleeding
Internal bleeding occurs when an artery or vein is damaged and blood to escapes the circulatory system and collects inside the body. Internal bleeding can be caused by a variety of situations such as blunt trauma, deceleration trauma, medications, fractures, and spontaneous bleeding. Treatment of internal bleeding depends on the cause of the bleeding.
Osteoporosis
Learn about osteoporosis, a condition characterized by the loss of bone density, which leads to an increased risk of bone fracture. Unless one experiences a fracture, a person may have osteoporosis for decades without knowing it. Treatment for osteoporosis may involve medications that stop bone loss and increase bone strength and bone formation, as well as quitting smoking, regular exercise, cutting back on alcohol intake, and eating a calcium- and vitamin D-rich balanced diet.
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis is a type of arthritis that causes chronic inflammation of the spine. The tendency to develop ankylosing spondylitis is genetically inherited.
Broken Toe
A broken toe is one of the most common fractures among individuals. There are many causes of a broken toe, whether it is the big toe, middle toes, or little toe (pinky). Common symptoms of a broken toe include pain, swelling, stiffness, and bruising. A broken toe can be treated with buddy taping the toe. There are instances where a physician should be consulted for a broken toe.
Shin Splints
Shin splints result from inflammation from injury to the tendon and adjacent tissues in the front of the outer leg. Shin splints commonly occur in runners or aggressive walkers, causing pain and discomfort. An increase in workout intensity, weak ankles and pronation may be to blame for shin splints. Stretching, strengthening, and icing the affected area are effective treatments for shin splints. Rest and anti-inflammatory medications are also advised.
Pleurisy (Pleuritis)
Pleurisy, an inflammation of the lining around the lungs, is associated with sharp chest pain upon breathing in. Cough, chest tenderness, and shortness of breath are other symptoms associated with pleurisy. Pleurisy pain can be managed with pain medication and by external splinting of the chest wall.
Paget's Disease
Paget's disease is a chronic bone disorder due to irregular breakdown and formation of bone tissue. Symptoms of Paget's disease include bone pain, headaches and hearing loss, pressure on nerves, increased head size, hip pain, and damage to cartilage of joints.
Coccydynia
Coccydynia is an inflammation of the bony area (tailbone or coccyx) located between the buttocks. Coccydynia is associated with pain and tenderness at the tip of the tailbone between the buttocks. Pain is often worsened by sitting. There are many causes of tailbone pain that can mimic coccydynia including: fracture, pilonidal cysts, infection, and sciatica. Treatment methods include medication and rest.
Muscle Pain (Myofascial Pain Syndrome)
Myofascial pain syndrome is muscle pain in the body's soft tissues due to injury or
Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis is an infection of the bone. Potential causes include injections around the bone, fractures that puncture the skin, recent surgeries, and bacterial infections that travel from other areas of the body, spreading through the blood to the bone. Symptoms include pain, fever, chills, stiffness, and nausea. Treatment involves antibiotics and pain medications. Surgery is sometimes necessary.
Frozen Shoulder
A frozen shoulder(adhesive capsulitis) is when the shoulder joint experiences a significant loss in its range of motion due to inflammation, scarring, or injury. Treatment involves anti-inflammatory medication, cortisone injections, and physical therapy.
Sprains and Strains
An injury to a ligament is called a sprain, and an injury to muscle or tendon is called a strain. Sprains and strains may be caused by repetitive movements or a single stressful incident. Symptoms include pain and swelling. Though treatment depends upon the extent and location of the injury, rest, ice, compression, and elevation are key elements of treatment.
Broken Foot
There are several bones in the foot, and these bones can be broken (fractured) in a variety of ways. Falling from heights, dropping heavy objects on the foot, or stress fractures from running or walking. Treatment of a broken foot depends on what bone in the foot is broken.
Osteopenia
Osteopenia is a bone condition characterized by bone loss that is not as severe as in osteoporosis. Bone fracture is the typical symptom of osteopenia, though the condition may be present without symptoms. Treatment involves lifestyle modifications (quitting smoking, not drinking in excess) and ensuring an adequate intake of vitamin D and calcium.
Head Injury
In the United States, head injuries are one of the most common causes of death and disability. Head injuries due to bleeding are generally classified by the location of the blood within the scull, these include: epidural hematoma, subdural hematoma, subarachnoid bleed, intracranial bleed, sheer injury, edema, and skull fracture. Some common symptoms of a head injury include: vomiting, bleeding from the ear, speech difficulties, paralysis, difficulty swallowing, and body numbness. Treatment of a head injury depends on the type and severity of the injury.
Hypercalcemia (Elevated Calcium Levels)
Hypercalcemia is a condition in which calcium levels in the blood are elevated. Hypercalcemia is associated with other conditions such as hyperparathyroidism, lung cancer, breast cancer, kidney failure, and elevated levels of vitamin D. Symptoms of hypercalcemia include constipation, nausea, abdominal pain, kidney stones, to name a few. Treatment depends on the cause of hypercalcemia.
More
Shaken Baby Syndrome
Shaken baby syndrome is a form of child abuse in which violent shaking of an infant causes the brain to move inside the skull, causing bruising of the brain and tearing of blood vessels. The shaking results in bleeding around the brain, bleeding in the eyes, spinal cord and neck injuries, bruises, and rib fractures. Infants who survive may suffer brain damage and blindness.
Facial Nerve Problems and Bell's Palsy
Facial nerve disorders affect the muscles of the face. There are many causes of facial nerve disorders including: trauma, nervous system disease, infection, metabolic disorders, tumors, toxins, or Bell's palsy. Symptoms of facial nerve problems include: facial muscle paralysis, weakness, or twitching of the face; dryness of the eye or mouth, or taste alteration.
Introducton
Chest pain is one of the most common complaints that will bring a patient to the Emergency Department. Seeking immediate care may be lifesaving, and considerable public education has been undertaken to get patients to access medical care when chest pain strikes. While the patient may be worried about a heart attack, there are many other causes of pain in the chest that the healthcare provider will need to consider. Some diagnoses are life threatening, while others are less dangerous.
Deciding the cause of chest pain is sometimes very difficult and may require blood tests, x-rays, CT scans and other tests to sort out the diagnosis. Often though, a careful history taken by the healthcare provider may be all that is needed to find the answer.
Source: www.medicinenet.com
No comments:
Post a Comment